Mastering Values, Leadership, and
Change» (ISBN-13: 978-1405133562)
The Project Roadmap® from www.gpm-ipma.de includes the Company and Project Organization and matrix of responsibilities!
The organizational structure helps to avoid situations where it is unclear who reports to whom and who is responsible for the performance of their subordinates.
Holistic description of the organization's activities
Organizational structure is a tool for managing people in a company or project; it is an organization chart with which linear subordination is visible.
The organization structure/diagram is part of the organization's activity model.
The model of the organization's activity is a set of interdependent and complementary graphical models of various types, each of which describes the existing situation in a particular subject area of activity.
A holistic description of the organization's activities can be performed according to the model developed by IDS SCHEER, which looks like this on one slide.
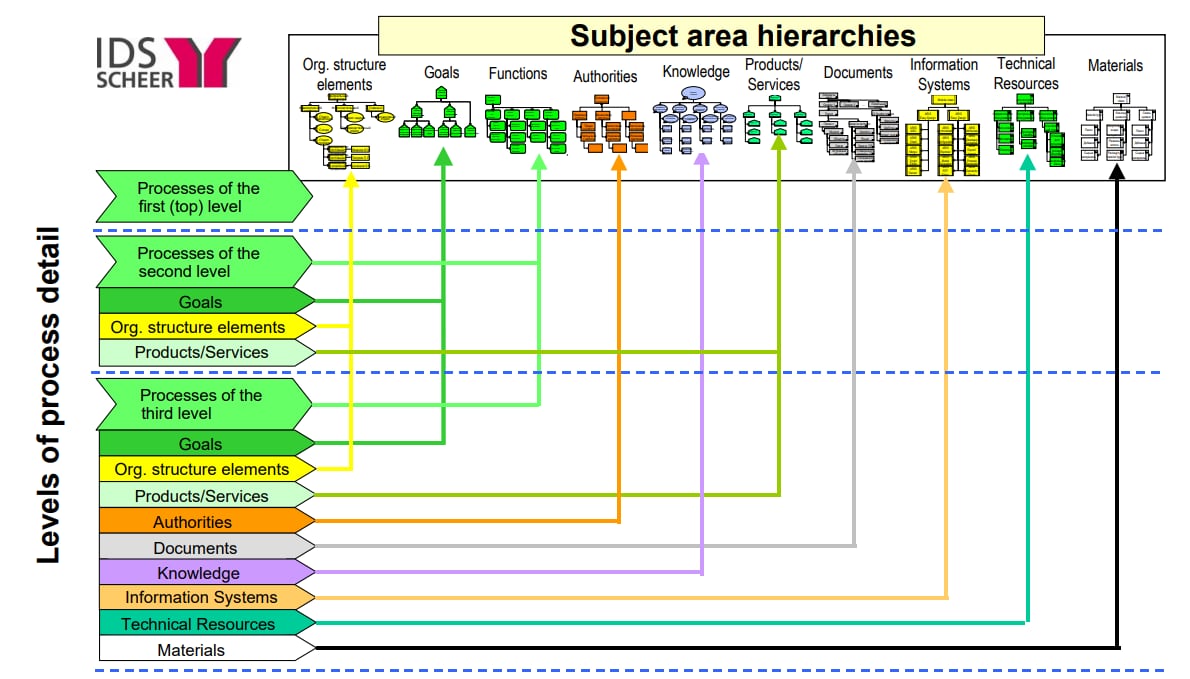
Organizational structure, regulations, job descriptions, functional responsibilities, and matrices of authority (responsibility) are just some reports from the organization model that are created and updated manually or automatically using Business process management software (BPMS).
Rules for the minimum required number of positions and people to unite them into organizational units and consolidate (aggregate) organizational units
The following types of organizational units are usually used:
Direction = minimum 2 departments (15 positions, 15 people)
Department = minimum 2 departments ( 7 positions, 7 people)
Desk = minimum 3 positions (3 people = 1 manager + 2 subordinate positions and a person)
Team = minimum 2 positions (2 people = 1 Team Lead + 1 Team Member)

| 15 positions, 15 people | 7 positions, 7 people | 3 positions, 3 people | 2 positions, 2 people |
 |  |  |  |
Remembering that the word minimum in determining the number of positions and people for each organizational unit means that there may be more. For example, a team may have 10 positions, but it will not be transformed into a department, although formally, admittedly, there will already be grounds for this. One such ground maybe this organizational unit's design or cross-functional inconstancy.
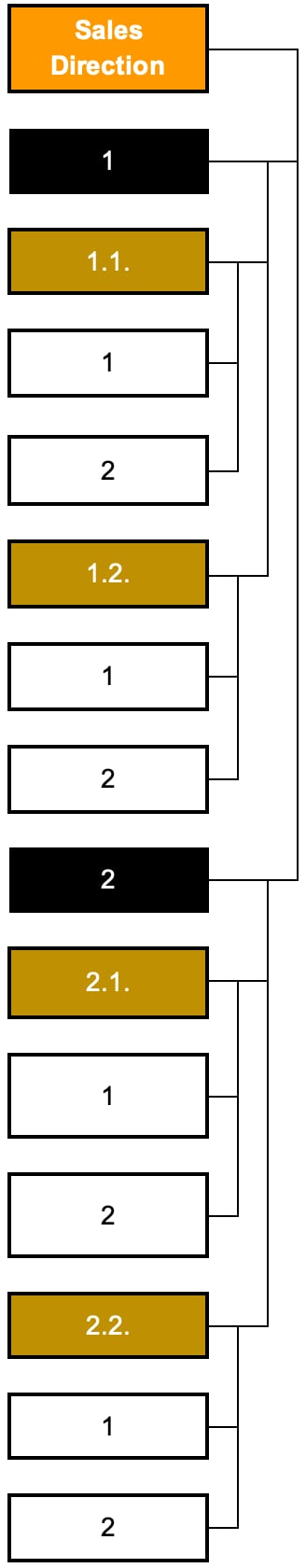
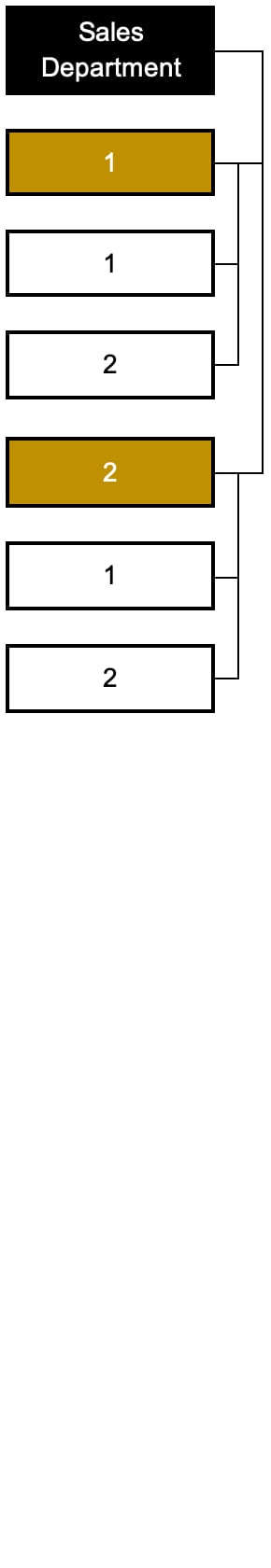
The rule for creating an organizational structure only by levels of units
In accordance with this rule, only unit names are indicated according to the color designation of the level of the organizational unit but not indicate the names of positions.
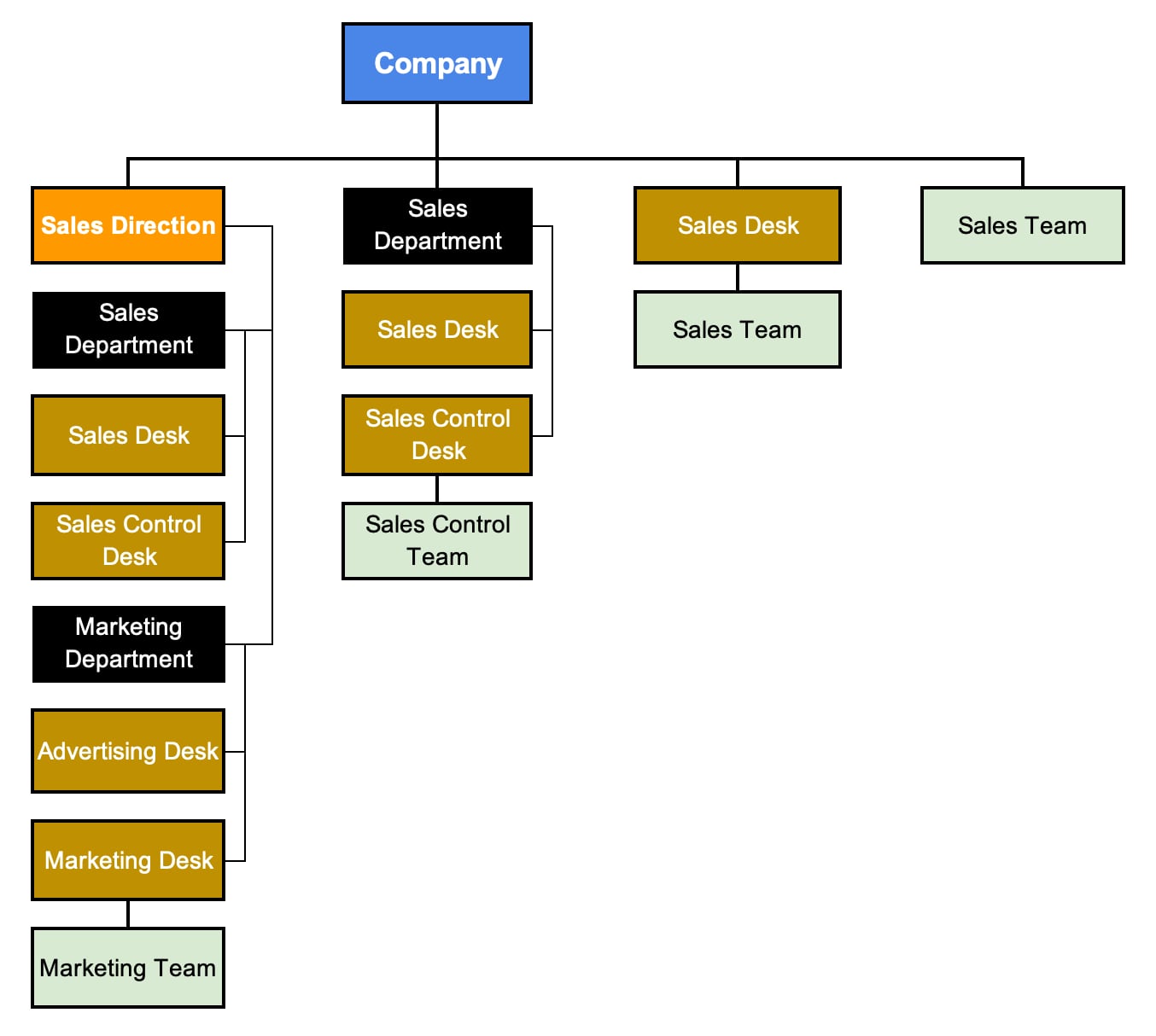
The advantage of this rule is the demonstration of the so-called bird's eye view, which allows you to compactly show all organizational units of the company.
The rule for creating an organizational structure only by the full names of positions of units
This rule details the organizational structure created only by unit levels.
In accordance with this rule, only the full names of positions of units are indicated in accordance with the color designation of the level of the organizational unit.
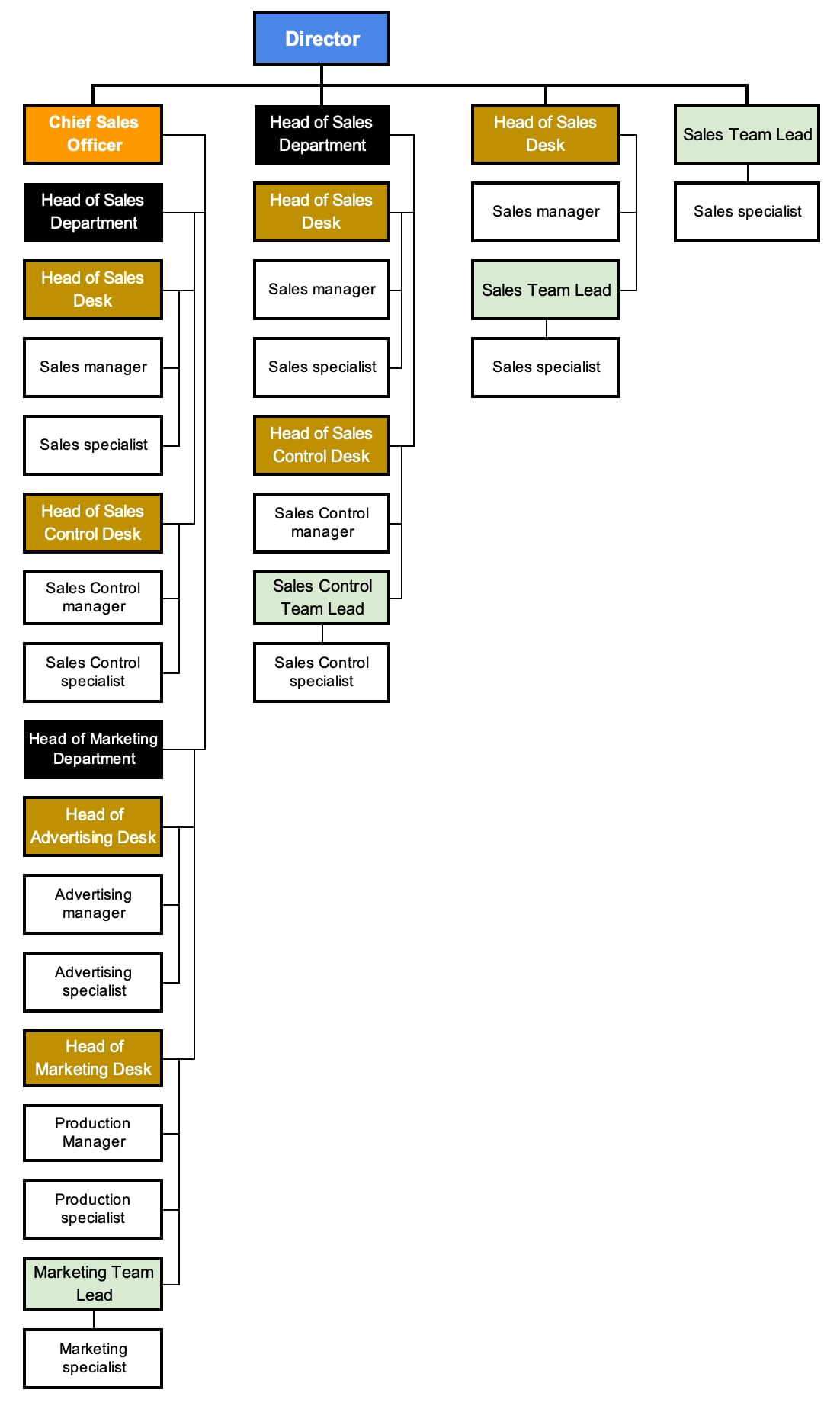
The rule for forming the names of organizational units
The business unit's name is appended to the principal business function name.
| Core business function | Organizational unit | Unit name |
| Sales | Direction | Sales Direction |
| Department | Sales Department | |
| Desk | Sales Desk | |
| Team | Sales Team | |
| Sub-team | Sales Sub-team |
The rule for forming job titles in organizational units
General rule: [Position level] + [Business Function] + [Position]
Directories
| Position level | Business function | Position | Organizational unit |
| Chief Lead Senior Middle Junior .......... Chief ->Lead -->Senior --->Middle ---->Junior | Technical Product Engineering Business Development Software Development Marketing Sales Human Capital Operation Finance Legal Project Process | Officer Head Manager Specialist .......... Officer ->Head -->Manager --->Specialist | Direction Department Desk Team Sub-team .......... Direction ->Department -->Desk --->Team ---->Sub-team |
For example: Chief + Technical + Officer
Using a combination of level and position allows you to build a career ladder within each business function, promising and ensuring company employees' career and professional growth.
| Position level | Business function | Position |
| Lead Senior Middle Junior | Marketing | Lead Marketing Specialist Senior Marketing Specialist Middle Marketing Specialist Junior Marketing Specialist |
SDTEST® allows you to determine in project managers the makings of a blue behavior model that is most appropriate to create the organisation structure. The higher the percentage in blue due to the SDTEST®, the more naturally the model of this person's behavior corresponds to the requirements to create the organisation structure.
